Author Archives: luxus
Subquantum Kinetics Predictions
Predictions Part II
physics and astronomy
Subquantum Kinetics Predictions
and their Subsequent Verification
Nucleon Core Field - prevailing concept (1978): The electric field in the core of a nucleon is assumed to be aperiodic and to rise to a sharp cusp at the particle's center.
Prediction No. 1 (1973 - 1978): Subquantum kinetics predicted that the electric potential field in the core of a subatomic particle should be Gaussian-shaped and should continue outward as a periodic field pattern of diminishing amplitude having a radial wavelength equal to the particle's Compton wavelength, further that this field pattern should be positively biased in positively charged particles. Prediction published in: 1985 (IJGS), 1994 (Subquantum Kinetics), and 1995 (Beyond the Big Bang).
Verification (2002): Particle scattering form factor data for the proton and neutron is found to be best fit by a model in which the nucleon core electric charge density distribution has characteristics similar to those that subquantum kinetics had predicted. Energy boosting during collision, however, did cause the target nucleons to exhibit a wavelength slightly shorter than had been predicted.
Energy Conservation and Photon Redshifting - prevailing concept (1978): At the time of this prediction, physicists and astronomers generally assume that photon energy is perfectly conserved and that the cosmological redshift is an effect arising from an assumed expansion of space.
Prediction No. 2 (1978): As a basic requirement of its methodology, subquantum kinetics predicted that photons passing through regions of more positive gravitational field potential where the reaction system is subcritical, e.g., intergalactic space, should progressively redshift with the passage of time, that is, undergo a "tired-light effect." The spectra of distant galaxies should then redshift even in the absence of any net recessional motion.
Verification (1979 - 1986): Dr. LaViolette checks this photon redshifting prediction by comparing the tired-light non-expanding universe model and the expanding universe model (standard Freidman cosmology) to observational data on four different cosmology tests. He demonstrates that the tired-light model consistently makes a closer fit to observational data on all tests. His findings, which were published in the Astrophysical Journal (1986), confirm the subquantum kinetics tired light prediction and the notion that the universe is cosmologically stationary. These findings undermine a key support of the big bang theory. An update of this evidence is presented in Chapter 7 of Subquantum Kinetics.
Energy Conservation and Energy Generation - prevailing concept (1978): At the time of this prediction, physicists and astronomers adhered to the idea that energy is perfectly conserved. Stars are assumed to generate their energy either through nuclear fusion or from heat released from gravitational accretion. Planets are instead thought to acquire their luminosity from stored heat. There is no reason to believe that planets should conform to the stellar mass-luminosity relation.
Prediction No. 3 (1978 - 1979): As a basic requirement of its methodology, subquantum kinetics predicted that photons should progressively blueshift in regions of more negative gravitational field potential where the reaction system is supercritical, e.g., within stars and planets and in interplanetary and interstellar space. It predicted that "genic energy" should be continuously created within all celestial bodies.
Verification (1979 - 1992): Dr. LaViolette tested this genic energy prediction by plotting the mass-luminosity coordinates of the jovian planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus) to compare them with the mass-luminosity relation for red dwarf stars and found that both planets and stars conformed to the same relation. Other astronomers had not previously done this because doing so didn't make sense in the context of the conventional astrophysical paradigm. This conformance suggests that the heat coming from the interiors of planets is produced in the same way as that radiating from the interiors of red dwarf stars, just as subquantum kinetics predicts. He also showed that the genic energy hypothesis predicts a slope for the "planetary stellar M-L relation" similar to the observed slope. In addition, he showed that the upward extension of the M-L relation predicts that about 16% of the Sun's luminosity should be of genic energy origin, an amount consistent with recent SNO solar neutrino measurements. The required violation of energy conservation is 10 orders of magnitude smaller than what could be observed in laboratory experiments.
Verification (January 1995): Astronomers observing with the Hubble Space Telescope discovered that the star VB10 has a dynamic core, as indicated by the presence of explosive, magnetic-field-driven flares on its surface. VB10 has a mass of about 0.09 solar masses, which indicates that it borders between being a red dwarf and brown dwarf. Conventional theory predicts that this star should be on the border of being dead and hence should not have a strong magnetic field. Subquantum kinetics, which predicts that its interior should be dynamic and actively evolving genic energy, anticipates these results.
Brown Dwarf Stars - prevailing concept (1985): At the time of this prediction, astronomers do not expect that brown dwarf stars to have any particular mass-luminosity ratio. They are assumed to be stars that are not massive enough to ignite nuclear fusion and hence are merely dead stars that are cooling off.
Prediction No. 4 (1985 - August 1995): Subquantum kinetics predicted that brown dwarfs should also generate genic energy and hence, like the jovian planets, should lie along the lower main-sequence mass-luminosity relation for red dwarf stars. Paul LaViolette published this prediction on four occasions: 1985 (LaViolette, IJGS, p. 339), 1992 (LaViolette, Physics Essays), 1994 (LaViolette, Subquantum Kinetics, p. 125), and 1995 (LaViolette, Beyond the Big Bang, p. 304).
Verification (November 1995, 1998): Astronomers determine the masses and luminosities of two brown dwarfs GL 229B and G 196-3B. Dr. LaViolette demonstrates that the M-L data points for these brown dwarfs lies along the planetary-stellar M-L relation as he predicted. This indicates that brown dwarfs are not dead stars as previously supposed, but stars that are actively producing genic energy in their interiors.
Interplanetary maser signals - prevailing concept (1985): Maser signals are believed to maintain constant frequencies over interplanetary distances since photon energy is assumed to be perfectly conserved.
Prediction No. 5 (1980): Dr. LaViolette determines the expected magnitude of the hypothesized genic energy photon blueshifting rate by modeling the intrinsic luminosities of the planets. He then predicts that if a maser signal were transponded between two spacecraft separated by 5 AU, the signal should be found to blueshift at the rate of about 1.3 ± 0.65 X 10-18 per second (equivalent to a blueshift rate of 1.1 ± 0.6 X 10-18 per second for signals traveling a 65 AU roundtrip journey. This prediction was published on two occasions: 1985 (LaViolette, IJGS, p. 340) and 1994 (LaViolette, Subquantum Kinetics, p. 135).
Verification (October 1998): A group of scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) publish their discovery that maser signals transponded between the Earth and the Pioneer spacecraft blueshift at a rate of ~ 2.9 ± 0.4 X 10-18 per second. Their value reduces to 2.3 ± 0.4 X 10-18 per second when the propulsive effects of waste heat from the spacecraft power source is taken into account. The predicted blueshift rate is within 2 sigma of the observed rate. LaViolette had discussed his prediction with one member of the JPL group as early as 1980. Although, the JPL team had apparently forgotten about the conversation and chose their own a posteriori interpretation of the phenomenon, conceiving the blueshift to be produced by a mysterious force continually pushing the spacecraft toward the Sun. Their observations nevertheless provide close confirmation of the a priori subquantum kinetics prediction; see paper posted at pioneer.html. For a detailed discussion see the Pioneer effect press release. A chronology of events of the Pioneer effect prediction and subsequent JPL verification is graphically depicted at the end of the press release.
Galactic Evolution - prevailing concept (1979):At the time of this prediction, astronomers believed that galaxies form in various sizes as galactic-sized gas clouds gravitationally condense to form stars. They assume that the size of these galaxies does not change over time except through galaxy mergers. Galaxies in the immediate neighborhood of the Milky Way are assumed to have the same size ratio as young galaxies at cosmological distances.
Prediction No. 6 (1979 - 1994): Subquantum kinetics predicts that matter is continuously created throughout the universe, with the matter creation rate being highest in the vicinity of already existing matter. Furthermore it predicts that galaxies should progressively grow in size with the passage of time since they are formed by matter being created primarily in their central nucleus and being propelled outward by galactic core explosions. Dr. LaViolette published this prediction on two occasions, in 1985 (LaViolette, IJGS, p. 335) and in 1994 (LaViolette, Subquantum Kinetics, p. 118). Also see LaViolette, Beyond the Big Bang, p. 94.
Verification (July 1995): Observations with the Hubble Space Telescope show that younger, more distant galaxy clusters are dominated by fainter, more compact galaxies and have much fewer of the larger spiral galaxies, as compared with nearby older galaxy clusters.
Galactic Core Energy Source - prevailing concept (1985): At the time of this prediction, the nuclei of active galaxies and quasars are known to contain central masses ranging from millions to billions of solar masses, and astronomers assume that these core masses exist in a collapsed state as black holes. They further assume that the prodigious energy output from these cores is powered from matter being swallowed by these hypothesized black holes. No other means of generating energy is known to explain the immense amount of energy observed to come from these locations.
Prediction No. 7 (1985): Subquantum kinetics predicts that matter-accreting black holes do not exist. Instead, it predicts the existence of highly massive, very dense celestial bodies of finite size called "mother stars" which continuously and spontaneously produce matter and genic energy in their interiors. LaViolette published his ideas on this on two occasions: 1985 (LaViolette, IJGS, p. 342) and 1994 (LaViolette, Subquantum Kinetics, pp. 143-144).
Verification (January 1995): A group of astronomers led by John Bahcall, observing with the Hubble Space Telescope, discover that 11 out of 15 quasars are devoid of any surrounding material and hence have no matter available to power a black hole hypothetically located at their centers. This supports the subquantum kinetics prediction that such energetic sources are instead powered by energy spontaneously created in their interiors.
Verification (September 1997): Hubble Space Telescope observations of the heart of active galaxy NGC 6251 provide further confirmation of the earlier January 1995 verification. These observations show that this galaxy's core is swept clear and hence that there should be no matter available to be accreted by a hypothetical central black hole.
Principles
Principles
The Starburst Foundation abides by the following operating principles:
- We shall convey through words, symbols and actions openness and respect toward all people. All our aims and objectives shall be achieved through peaceful and non-political means.
- We shall recognize each race or nation, in thoughts, words and deeds, as an essential part of the whole of humanity.
- We dedicate ourselves to creating peace and harmony by seeking unity beyond political, religious and social bias.
- Our objectives shall be carried out in a manner which recognizes the essential equality and uniqueness of every human being. Loving kindness, friendship, practical cooperation and sharing shall prevail.
- The practical results of our research will be utilized for the furtherance of world peace and prosperity.
- In our work we shall abide by international law, and by the laws of all nations in which we operate.
- We are aligned to serve responsibly in meeting the needs of evolving humanity, living in harmony with all realms of nature as stewards of our planet.
Book Review of Subquantum Kinetics by Hal Fox
Book Review of Subquantum Kinetics
by Hal Fox
Journal of New Energy
Paul A. LaViolette, Ph.D., SUBQUANTIUM KINETICS, A Systems Approach to Physics and Cosmology, 318 pages, 412 refs, Starlane Publications, Schenectady, NY, c2003, ISBN 0-9642025-5-7. $24
The number of references cited and provided by the author is a strong indication of the enormous effort that Dr. LaViolette has provided in the development of this remarkable theory of Subquantum Kinetics. The author appropriately cites these many references throughout the development and application of his theory.
LaViolette takes chemical kinetics concepts (such as nonequilibrium thermodynamics) and for the first time introduces these concepts into microphysics. The result is a new theory that postulates subquantum reaction processes as the basis of physical existence. The results of this novel treatment are summarized in an extensive table (Table 10) in the Conclusions in Chapter 12. Table 10 cites 30 topics that are not explained by other theories but are explained by Subquantum Kinetics. This book is worth the price just for this table listing the physics problems faced and unexplained by current theories. Any college student (or a former college student) of physics MUST become aware of the gaps in our currently-taught theories of physics if we are to make appropriate progress in the understanding of the universe where we have our being. Therefore, this book should be in every college library.
The eleven chapters preceding the Conclusion, describe in detail the development of the subquantum kinetics theory (Chapters 1-3) and then continue to provide details in the discussion of the following topics:
Chapter 4, Emergence of Particles and Fields.
Chapter 5, Fields and Forces.
Chapter 6, Energy Wave Behavior.
Chapter 7, The Cosmological Redshift.
Chapter 8, Matter Creation.
Chapter 9, Genic Energy (Energy creation in massive bodies).
Chapter 10, Stellar Evolution.
Chapter 11, Electrogravitics.This last topic is of special importance to this reviewer. As editor of the Journal of New Energy, it has been a privilege to print conference proceedings and submitted papers that allude to this highly interesting topic.
Dr. LaViolette has done an excellent job in discussing and citing the scant literature reporting on the development of thrust by the use of high voltage. The work of T. Townsend Brown is better covered in Chapter 11 than in any other publication that this reviewer has read. The book is worth its price just for this excellent description (and list of references) of the mostly- secret development of Brown's work. According to some of the reports (and personal sightings) about "flying saucers" there is substantial evidence that the shape of these flying objects is important and that high voltage is apparently used. Of the several reports of crashes of such vehicles, it is often associated with lightning or thunderstorms. The author's chapter on electrogravitics is an important contribution to the understanding of this work (mostly accomplished with the highest secrecy by the U.S. and Soviet Union). Here again, this reviewer suggests that this information is worth the price of the book.
The work accomplished by A. Einstein on Special Relativity and General Relativity was done mainly during the 1905 to 1920 period. It should not come as any surprise to any reader to find that Einstein's work is subject to improvement. This book cites some specific examples where it is necessary to move beyond (or make some corrections in Einstein contributions) to resolve some of the challenges of Physics. [It is well known to this reviewer that two of the basic postulates accepted by Einstein are false - that space is empty and that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum.] As the author states, we must move beyond the dogmatic acceptance of relativity and make some changes in our theories if we are to better explain some of the "unexplainable" topics in physics.
The author does an outstanding elaboration of the concepts that lie (pun intended) with the Big Bang hypothesis. One of this reviewer's favorite quotes from this book is the following: (page 186) "Yet according to the big bang cosmology, a galaxy at a 3.4 redshift would have an age of just over one billion years. Big bang cosmologies, then, must explain how a galaxy that is about one billion years old could contain stars that are over 12 billion years old."
As an eighty-year old student of physics, this reviewer strongly welcomes Dr. LaViolette's contribution to a much better understanding of the many unexplained problems in physics and a theory that can be used to unravel these long-standing mysteries. This book is highly recommended. However, don't expect that this presentation will be the last and final explanation of the universe in which we live. There will still be some surprises to come and some additions and modifications to the best theories (of which this must be one).
Book Review of Subquantum Kinetics by Prof. Eugene Podkletnov
Book Review of Subquantum Kinetics
by Prof. Eugene Podkletnov
Infinite Energy magazine
Short review of the book "Subquantum Kinetics"
by Paul LaViolette
The book by Paul LaViolette is a serious scientific study which examines the problem of the interaction of solid bodies and electromagnetic fields with the physical vacuum, taking into consideration an extremely large portion of the theoretical and experimental knowledge of modern physics. The need for this book has existed for a long time because an enormous volume of experimental data accumulated during the last half of the century in physics, chemistry, cosmology and material science does not fit the concepts of the more familiar theories of quantum mechanics, plasma physics, superconductivity, light as well asEinstein's general and special relativity theories.
The scientific world in the 21st century continues to develop in accordance with the laws of dialectics, the general volume of data in the field of physics eliciting a transformation wherein quantitative changes evoke qualitative ones to result in new theories. One of these overwhelming theories is the theory of the "physical vacuum" or ether, in other words the theory proposing that sub-atomic particles fill all the space around us and actively interact with material objects and fields, changing their properties, energy, and speed, and directly influencing physical and chemical reactions. The appearance of such terms as physical vacuum, vacuum polarization and vacuum energy fluctuations was met by many scientists as a challenge to existing theories and for many years these terms were not accepted by official science. Many aspects of the statements about the physical vacuum were considered to contradict the "logical statements" of quantum mechanics, Einstein's theory and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. At the same time physicists preferred not to discuss the well known and extremely great contradictions that exist between quantum mechanics and Einstein's theories. As all modern electronic science is based on quantum mechanics and as nuclear energy is based on Einstein's formulas, both of these approaches were considered flawless and attempts to explain the mechanism of physical phenomena in terms that have used new approaches, have been punished severely.
Nevertheless, a large volume articles in serious magazines in the USA, in Europe, and in Russia have concluded that the question of understanding the physical vacuum is the greatest problem of modern physics and deserves careful consideration. Besides, practically all of the physicists of the 19th and 20th centuries, including Einstein, accepted the existence of an ether.
The investigation of the physical vacuum is important for several reasons: it allows us to eliminate the various contradictions of modern physics because it describes the interaction of elementary particles, formulates the main concepts and the laws of the world of sub-atomic particles, describes the processes of energy exchange, explains the mechanism of generation and propagation of electromagnetic, nuclear and gravity fields, and the initial creation of matter. Therefore it introduces the possibility of using the energy of the vacuum for the elaboration of new, unique technologies in physics and chemistry and allows us to operate directly with the structure of a solid body and, based on entirely new principles, to extract energy with an efficiency several orders of magnitude higher than that achieved at present.
The detailed understanding of the mechanism of gravity will allow us to use this knowledge for the creation of a fast communication network as well as for the creation of new flying vehicles, and the elaboration of new methods of building technology and cargo transportation. The main questions of the energy of the physical vacuum have been addressed in articles by American scientists, such as Bernard Haisch, Harald Puthoff and Alfonso Rueda. Their works in the field of zero point energy fluctuations of the vacuum can be regarded as a classical approach to this field of knowledge. The extremely serious work of Dr. Dyatlov from Russia concerning the polarization of the physical vacuum can be considered as a practical continuation of these theories.
The book on subquantum kinetics by Paul LaViolette is one of the first profound works in this field. Usually the analysis of the corresponding material requires complex mathematical equations, and many articles typically contain an abundance of integrals, which doesn't always help to reveal the essence of the physical phenomena. A great merit of Paul LaViolette is his ability to discuss the main features of the subatomic world without using complex mathematics and while preserving a rigorous logic in his arguments and conclusions. That doesn't mean that the book is primitive. On the contrary, in order to understand the full scope of the discussed phenomena, it is helpful to have a profound knowledge of solid state physics, electricity, optics, chemistry, and elementary particle physics.
This book should be of value to various physicists ranging from professors to students of technical universities and is an important manual for engineers and researchers as it contains the information and background for inspiring new experimental works. There are grounds to recommend this monograph as a compulsory textbook for students of the physical sciences because without knowledge of the main aspects of subquantum kinetics, modern physics will not adequately develop as a science and also because the detailed understanding of physical phenomena and their complex interrelations is a basic requirement for every expert in the field of physics.
On the other hand, if we analyze this book taking into consideration only well-known scientific facts, it may seem that the problem of subquantum physics doesn't exist. Up to the present, vacuum has widely been regarded as an absolutely empty space or nothing. Students were taught using this approach, many Ph. D. degrees were earned, and everything seemed to be fine, but frankly speaking, there has been little progress in the field of physics during the past 40 years. Meanwhile, the communication with spacecraft on the surface of Mars is based on electromagnetic waves. The wave, by conventional definition, is a distortion of space; if there is no space, there is nothing to distort. According to Einstein, gravitation is a geometrical bending of space-time, and we accept it. But if space is absolute emptiness, it is impossible to bend it. This is pure logic. But if we refer to the handbook for physics, we will find that an empty vacuum has more than 10 different characteristics, including a dielectric constant, modulus of elasticity, magnetic permeability coefficient, magnetic susceptibility, modulus of conductance, a characteristic electromagnetic wave impedance of 377 Ohms, and other values. Isn't that much for an absolutely empty space?
From my discussions with nuclear physics experts at accelerators in Dubna, also from CERN and Fermi National Labs, I understood that all of them accept the idea of a physical vacuum not as a theory, but as an experimental fact. This approach is shared by many NASA experts and by a large fraction of the researchers from American, Russian and European universities.
In autumn of 2002, there appeared a book by Dr. Bearden "Energy from vacuum" having a length of 977 pages and it has become a bestseller in the scientific media, despite its price of over 100$. Thomas Bearden, retired colonel, who has diplomas in nuclear physics, mathematics, and engineering, presents an analysis of 30 years of his studies in the field of new technologies and energy production. The impact of this work is great and it's influence on modern readers can't be denied, but with all its good qualities, this book is more a popular than a scientific one, and the author didn't have the intention of giving a profound scientific approach. Although the book by Paul LaViolette, , doesn't contain nice color illustrations, it nevertheless concentrates on the scientific analysis and comparison of mechanisms and interactions between sub-atomic particles and ordinary matter and is therefore an extremely important and useful tool. This book teaches us how to think about and understand the physics and the nature around us, and more importantly - this is just a beginning, one that provides the basis for further development, further study, and new experiments, following a systematic and scientific approach. There is no doubt that this book is an outstanding contribution to modern physics and that it will receive the attention and appreciation of many thankful readers.
Evgeny Podkletnov, Ph.D.,Tech.D., Professor of chemistry
Tampere, Finland
Research Areas
Research Areas
The Foundation is pursuing the following projects:
- Astronomy and Climatology: The Foundation is investigating Galactic superwaves [cosmic ray outbursts from the Galactic Center] and their past effects on the Earth's climate and biosphere. Starburst is:
- publishing technical papers that relate to the superwave phenomenon, abrupt climatic change during the ice age, and the cause of the Pleistocene megafaunal extinction,
- accumulating astronomical and geological evidence supporting the existence of superwaves in our Galaxy and in other galaxies, and
- communicating these findings to scientists, governmental institutions, and the general public through technical journal publication, personal correspondence, television interviews, news media releases, and lectures.
- The Foundation is interested to conduct a polar ice core analysis study to determine how cosmic dust, terrestrial dust, and beryllium-10 have varied in concentration over time and to determine how such variations correlate with abrupt changes of climate, geomagnetic field excursions, and animal extinction episodes. This would provide much needed information about how superwaves have affected the Earth in the past.
- Physics and Astronomy: The Foundation is researching subquantum kinetics, a new physics methodology that offers a novel approach to understanding nature at the quantum level. Starburst is:
- Publishing technical papers that apply the subquantum kinetics methodology to the description of both microphysical and astronomical phenomena thereby resolving many long-standing paradoxes of physics and offering a new, more satisfying explanation for the origin of the physical universe; networking these findings to scientists, governmental institutions, and the general public,
- Planning a research study that would experiment with computer software that would simulate subquantum, reaction-diffusion processes, thereby producing visual images of particle-like structures that would behave similarly to subatomic particles and realistically display particle-field interactions.
- Extraterrestrial Communication: Evidence has recently been disclosed which suggests that radio pulars are communication / navigation beacons of extraterrestrial intelligence origin; see Decoding the Message of the Pulsars by Paul LaViolette. The Foundation is interested in further investigating evidence that pulsar signals may be conveying intelligent information. Also we are interested in establishing contact with civilizations transmitting these signals.
- Psychology and Education: The Foundation has promoted the feeling tone conception of mental process, a novel theory that resolves the long-standing mystery of how the human mind is able to produce creative thought and that emphasizes the significant role feelings play in this process.
Systems Psychology: Feeling Tone Theory
Various researchers comment about Emotional-Perceptive Cycle Theory
View their comments
The article below appeared in the newsletter On the Beam
Teaching with Feeling in Mind
(Reprinted from On the Beam, Volume 6(2) (1986))
.
Our approach to teaching is strongly influenced by your understanding of how the human mind functions to form thoughts. Modes of classroom instruction currently in widespread use are based upon the outdated "robot model," which views the brain as an input-output information storage and processing unit. Computer analogies, however, are unable to account for a key feature of intelligence, one that is central to the learning process, the phenomenon of creative thought formation.
Recently, however, a novel theory has been developed which sheds some light on the creative process. This theory conceives creative thoughts as emerging spontaneously from a fabric of sensation and emotion composed of experiential units called "feeling tones." According to Bill Gray,(1) basic feeling tones, like the primary colors of the rainbow, combine in a nearly infinite number of ways to form a whole spectrum of shades and these represent all aspects of our internal and external experience. Just as Mozart's 41st symphony and Beethoven's 9th may both be played from the same set of musical notes, so too the rich variety of mental experience that bombards our consciousness may be represented by means of the same fundamental set of feeling tones.
Like people and cars in a city, these complex feeling tone structures , or "compositions," are always on the move through our brain. Just as a well-designed city allows people to meet one another and form rich sets of associations and relationships, so too the brain provides an environment within which feeling tones are able to link up with one another and spontaneously form more complex combinations of a meaningful nature. These syntheses are what we call thoughts.
Robot model theorists conceive thoughts to be neuroelectric impulses which, like the binary coded electrical impulses in a computer circuit, derive their various meanings by travelling along specific "wires" or nerve fiber pathways. However, this hard-wired mechanistic conception unfortunately leads to a physicalistic view of the mind, conscious experience being conceived as inextricably bound to the physical architecture of the brain. The feeling tone model, on the other hand, conceives the meaning of thoughts to be intrinsic to the thoughts themselves, the information content of a thought being embodied in its specific feeling tone code or neuroelectric waveform shape. Like their feeling tone relatives, thoughts are on the move too. Thus mental information is portable and free to move throughout the brain.
According to this new view, the brain may be conceived as a kind of sophisticated loom, one which is suited to the weaving of mental fabrics.(2, 3) However, this is a very unusual loom. For, these feeling tone tapestries have the unique ability of themselves being able to run the controls of the loom. Thus the fabric is able to weave itself in a self-determining fashion! Because of this self-referential process, the mind is capable of independent evolution to states of complexity far exceeding that of its biological matrix, the brain.
The brain/mind relation in many ways resembles the mother/child, womb/embryo relation. The brain provides a unique environment within which that living entity the mind is spawned. Unlike embryonic development, however, there are no pre-existent chromosome blueprints. Rather, the "genes which shape the mental personality are continuously created on-the-spot, these spontaneous birth events being our creative insights and ideas.
It goes without saying that such a model of mental phenomena suggests an approach to education quite different from that currently practiced in schools. According to this approach, understanding is best accomplished through a process of facilitation, rather than through rote instruction. Teaching is not a programming process, the feeding of information into computer-like brains. Rather, it is an agrarian process -- the acquisition of knowledge being likened to the raising of crops. The teacher's purpose is to provide sunlight, fertilizer, and water, and an environment free of predators in which sensitivity, caring, and curiosity are free to develop. The learning which ensues must be viewed as a birth process, one which must not be rushed. Confusion results if material is delivered at a pace faster than the student can assimilate, since the evoked thoughts require sufficient time to take full root in the student's personal feeling tone fabric that he is perpetually weaving.
1) Gray, William "Understanding creative thought processes: An early formulation of the emotional-cognitive structure theory." Man-Environment Systems 9 (1979):314.
2) LaViolette, Paul A. "Thoughts about thoughts about thoughts: The emotional-perceptive cycle theory." Man-Environment Systems 9 (1979):1547.
3) LaViolette, Paul. A. "The thermodynamics of the aha experience." Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Society for General Systems Research, San Francisco, Jan. 1980; Reprinted in: (1982) W. Gray, et al. (eds.) General Systems Theory and the Psychological Sciences (Vol. I). Intersystems Press, CA.
Conventional Energy: Solar Energy
Alternative Energy Research
Solar Water Desalination Project
Conducted by the Starburst Foundation at a California Water Institute research site on the campus of California State University at Fresno.
Project conducted in 2004-2005, directed by Paul LaViolette
Funded by the California Energy Innovation Small Grants Program
Project Report 1.4 Meg pdf download
Research Equipment For Sale
Advanced Propulsion: Electrogravitics
Electrogravitics and Field Propulsion
Starburst research has advanced our understanding of the physics behind electrogravitics and other propellentless field propulsion technologies which makes possible the design of advanced aerospace propulsion technologies that could radically change our future means of travel. Imagine flying from New York to Sydney, Australia in 15 minutes or traveling to Mars in 5 days. These should no longer be considered wishful dreams, but realities of the present that are awaiting our implementation. To move forward, to make these dreams a reality, we must free ourselves from the outdated physics theories and paradigms of the past for which such technologies are an impossibility. The Starburst Foundation is helping to pave the way to this future through its development of subquantum kinetics, the first unified field theory to predict a coupling between electric and gravitational fields. Starburst researcher Paul LaViolette has shown that subquantum kinetics provides the basis for understanding the electrogravitic propulsion experiments of Thomas Townsend Brown, Jean-Claude Lafforgue, Eugene Podkletnov, John Searl and others. Some of these technologies, such as those of Brown and Lafforgue, provide thrust to power ratios ranging from 10,000 to 300,000 times that of the Space Shuttle's main engine. By providing a theoretical underpinning for the phenomenon of electrogravitic and electric field propulsion, subquantum kinetics lays the foundation for engineering the air and space vehicles of our future.
- Townsend Brown’s electrokinetic flying disc demonstration. Image taken from Brown’s U.S. patent.
- Townsend Brown’s pulsed DC levitating disc. _ © 2008 P. LaViolette
Townsend Brown's Project Winterhaven Report to the Navy (1.2 Mb)
Townsend Brown's work on Project Montgolier in France (1955 - 1956)

The 1956 air intelligence report Electrogravitics Systems obtained in 1985 from Wright-Patterson Air Force Base
In 1985, shortly after learning about the work of T. T. Brown, LaViolette stumbled upon a formerly classified 1956 think tank report entitled Electrogravitics Systems. This incredible document, which he obtained from Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, detailed the existence of a vast R&D program in the 1950's participated in by most of the major aerospace companies that was geared toward the practical application of this field propulsion technology for aerospace flight. Through his subsequent publications he brought to the attention of the public and scientific community the eye opening revelations contained in this report. In 1990 he participated in NASA's Space Exploration Outreach Project to inform NASA administrators about the existence of electrogravitic technology and of past aerospace industry involvement, as disclosed in this 1956 report. He proposed that NASA should seriously consider this energy-efficient means for space travel as a feasible alternative to rocket technology. Two years later, following an impromptu public disclosure of classified information by two black project engineers, LaViolette was able to successfully reverse engineered the propulsion system of the highly classified B-2 Advanced Technology Bomber. In a 1993 science and technology conference paper, he showed that the B-2 utlized as its propulsion system the electrokinetic technology that Townsend Brown had displayed in his early 50's flying disc experiments and whose application to aviation was detailed in U.S. patent No. 3,022,430 filed in 1956.

The B-2 Advanced Technology Bomber. In 1993 Paul LaViolette demonstrated that it is propelled by T. Townsend Brown's electrokinetic technology
In 1992 Dr. LaViolette directly contacted NASA's National Aero-Space Plane Project and attempted to interest them in using electrokinetics technology in their program, but without success; see letter from Charles Morris. The following year he again sent a packet of material to the Aero-Space Plane Project, specifically pointing out in his letter that one of the advantages of use of this technology is that it would be able to reduce frictional heating of the wing leading edge during reentry; see second letter to Charles Morris. Again, he was unable to raise any interest even though he had acknowledged that they had a problem with frictional heating of the spacecraft hull. Ten years later in 2003, the Columbia Space Shuttle disaster occurred. The cause of the mishap was excessive heating of the wing leading edge due to dislodgment of a heat resistant tile. Had NASA implemented electrokinetics technology at the time LaViolette had alerted them, this disaster would have been avoided. LaViolette submitted to the Columbia Accident Investigation Board a white paper informing the board about this technology and his previous efforts to inform NASA about it. As a response, he received back just a form letter thanking him for his input.
- ……. First Letter from Charles Morris …….
- ……. Second Letter to Charles Morris …….
Dr. LaViolette has shown how the subquantum kinetics field potential concept is able to explain why an assymetrical capacitor will develop a propulsive force towards its larger electrode when energized with a high voltage potential. Standard field theory acknowledges that the electric forces on such a capacitor will be unbalanced, but leads to the belief that these will merely produce stress within the capacitor without any propulsive force. In subquantum kinetics, these field potentials are anchored in the space surrounding the capacitor (in the surrounding ether) and as a result the capacitor is free to move in response to the resulting imbalance of forces. This explains the thrust seen in Brown's assymetrical capacitors tested by Townsend Brown as well as those tested by Jean-Claude Lafforgue. Tests of the Lafforgue asymmetrical capacitor have been carried out by Jean-Luc Naudin; see his website. These technologies routinely violate Newton's third law.
Early prediction of Pioneer anomaly challenges energy conservation law
For Immediate Release (Science)
February 20, 2007
Early prediction of Pioneer anomaly
challenges energy conservation law
Pioneer's encounter with Jupiter - Artist's rendition. Source: NASA
***********************************
Contact: The Starburst Foundation
plaviolette@starburstfound.org
Further information on this topic is found in the paper:
Paul A. LaViolette, Ph.D, "The Pioneer maser signal anomaly: Possible confirmation of spontaneous photon blueshifting."
Physics Essays 18(2) (2005): 150-163. In print as of January 2007.
Preprint: https://arxiv.org/abs/physics/0603191
Journal download: https://www.physicsessays.com
In 1979, while still a doctoral student at Portland State University in Portland, Oregon, Paul LaViolette made a prediction, which like Einstein's prediction of the bending of starlight may one day be destined to shake the world. At that time, he was developing a unified field theory called subquantum kinetics.(1-3) Unlike string theory, which has never made any testable predictions, LaViolette's subquantum kinetics theory has made a number of apriori predictions, ten of which have thus far been confirmed.(4) One in particular challenges the most fundamental of physical laws, the law of energy conservation. Subquantum kinetics predicts that a photon's energy should not remain constant but rather should change with time, that photons traveling through interstellar space or trapped within stars or planets should continually increase in energy, although at a very slow rate. For example, his theory predicts that a photon traveling through our solar system should increase its energy at a rate of somewhat greater than one part in 1018 per second.
A year later in 1980 LaViolette devised an experiment to test for the effect. This involved transmitting a maser (microwave laser) signal back and forth between a pair of spacecraft, one located near the Earth and the other located near Jupiter. The entire round-trip signal path would be sufficiently long to produce a detectable blueshift which could be checked to see if his theory was correct. A description of his experiment later appeared in a paper that was published in 1985 in a special issue of the International Journal of General Systems.(1)
JPL scientist John Anderson, who had been routinely monitoring spacecraft maser signal tracking data to look for evidence of gravity waves, later began to notice that a blueshifting effect may be present in the Pioneer 10 data. In 1992 his team began a formal statistical study to investigate the matter further, and in September 1998 they publicly announced that they had found a persistent unexplained blueshift in the maser signal data being transponded back from the Pioneer spacecraft. Anderson's paper was published a month later in the journal Physical Review Letters.(5)

Paul LaViolette at Portland State University after graduation in 1983.
This "unexplained" phenomenon has come to be known as the "Pioneer effect" or as the "Pioneer anomaly." Hence the NASA JPL findings were a direct confirmation of the effect that LaViolette had sought. As LaViolette notes in his paper which appeared recently in the journal Physics Essays,(6) the frequency blueshift observed in Pioneer spacecraft maser signal data was within two standard deviations of the amount he had predicted as early as 1980.
The JPL group attributed this blueshift to an anomalous force accelerating the spacecraft toward the Sun. In his Physics Essays paper, LaViolette points out that their anomalous force interpretation is problematic since, if a force of the magnitude they proposed were present, it would also necessarily be pushing the planets towards the Sun and cause their orbital periods to accelerate. But the planetary orbital periods are known to very high precision, and astronomical data shows that no such orbital acceleration effect is present, a point also acknowledged in Anderson's paper.
Imagine a photon's energy to be like money that you put in a bank. According to subquantum kinetics, if you come back in a billion years, the photon will have earned 10% interest. That is, you will find the photon to be 10% more energetic. This excess energy is a violation of the law of energy conservation, the First Law of Thermodynamics, which requires that the photon should have the same energy no matter how many billions of years your photon money is left in the bank. While the rate of energy change that LaViolette proposes is far too small to measure in the laboratory, if present it would be extremely significant for astrophysics. Essentially, it would require that astrophysicists scrap all their existing theories on stellar evolution and stellar energy production. Although the energy excess produced by any given photon each second would be incredibly small, when the cumulative effect of trillions upon trillions of photons inside a planet or star are added up, the amount of energy becomes quite sizable. LaViolette coined the term "genic energy" to refer to this spontaneously created energy which he says should be continually produced within all celestial bodies and which can account for most if not all of the energy radiated by planets and red dwarf stars.
An early test of the genic energy prediction he conducted in 1979 determined whether planets such as Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune might be producing energy in their interiors. The answer was affirmative. Infrared telescope measurements made by various spacecraft showed that indeed the planets radiated substantial amounts of heat from their interiors. As a further test, in 1979 LaViolette plotted the mass-luminosity coordinates for each of these planets along the mass-luminosity trend line for red dwarf stars. They conformed to this relation just as his theory predicted. This conformance is unexplained by standard theories, leaving the genic energy concept to be the only viable explanation. In fact, it was by performing a model fit to this planetary-stellar M-L data that LaViolette was able to derive a numerical value expected for the rate of photon blueshifting in interplanetary space.
Routinely the U.S. Patent Office rejects patents on so called free-energy devices that claim to generate energy without burning any kind of fuel by citing violation of the First Law of Thermodynamics. Even though the inventor in many cases provides signed affidavits of witnesses claiming to have tested the device, many inventions which might provide us with an alternative to burning hydrocarbon fuels end up in society's trash bin. By substantiating LaViolette's earlier work, JPL's findings cast doubt on the absolute validity of this law. With global warming well upon us, it is time the physics community gives serious consideration to LaViolette's prediction.
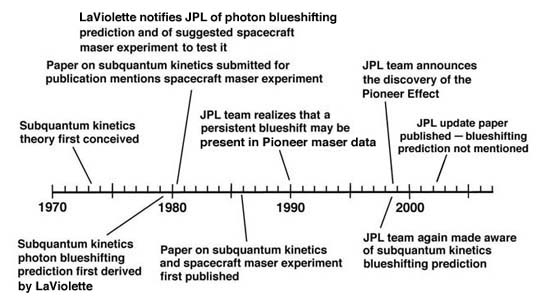 |
Time line indicating date of LaViolette's prediction and date of its verification by the JPL team.
References
1) Paul A. LaViolette, "An introduction to subquantum kinetics." Parts I, II, and III. International Journal of General Systems 11 (1985):281-345.
2) Paul A. LaViolette, Subquantum Kinetics: A Systems Approach to Physics and Cosmology (Niskayuna, NY: Starlane Publications, 1994, 2003); https://starburstfound.org/LaVioletteBooks/Book-SQK.html.
3) Paul A. LaViolette, Genesis of the Cosmos: The Ancient Science of Continuous Creation (Rochester, VT: Bear & Co., 1995, 2003); https://etheric.com/LaVioletteBooks/Book-BBB.htm;
https://www.curledup.com/gencosmo.htm.
4) See list at: https://starburstfound.org/predictions-part-2/.
5) John D. Anderson, et al., Physical Review Letters 81 (1998): 2858-2863; Eprint https://arXiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9808081.
6) Paul A. LaViolette, "The Pioneer maser signal anomaly: Possible confirmation of spontaneous photon blueshifting." Physics Essays 18(2) (2005): 150-163.
Galactic Superwaves and Core Explosions
Galactic Superwaves
One principal area of research that the Starburst Foundation is involved with is the investigation of Galactic superwaves, intense cosmic ray particle barrages that travel to us from the center of our Galaxy and that can last for periods of up to several thousand years. Astronomical and geological evidence indicates that the last major superwave impacted our solar system around 12,000 to 16,000 years ago and produced abrupt changes of the Earth's climate. It is estimated that approximately one or two superwaves strong enough to trigger an ice age are presently on their way to us from their birth place 23,000 light years away. There is a finite chance that one such event could arrive within the next few decades.
Less intense superwaves, which recur with considerable frequency, could also pose a threat. There is evidence that the Galactic Center has erupted as many as ten times in the past two millennia, the most recent event occurring about 700 years ago. While these low intensity events could have passed unnoticed in earlier centuries, today they could be extremely hazardous. The electromagnetic radiation pulse accompanying such a superwave would be far more intense than any gamma ray pulse we have experienced in modern times. It could knock out electrical power grids and communication networks on a global scale and possibly even inadvertently trigger nuclear missile launchings. Consequently, study of this phenomenon deserves a very high priority.
Starburst researcher Dr. Paul LaViolette began alerting the scientific community to the existence of superwaves in 1983 through his published papers and scientific conference presentations (see paper archive). He also raised the public awareness about the superwave phenomenon through his book Earth Under Fire as well as through various magazine articles.
Many aspects of Dr. LaViolette's superwave theory have since been verified by various observations; see the following list of predictions and their subsequent verification.
Further information












